William Cheng, Director of Enterprise Marketing
Contact UsIn the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), data stands as the lifeblood of innovation. As AI algorithms grow more sophisticated and data-hungry, the necessity for high-performance storage solutions becomes increasingly critical. Here's why:
The Data Deluge in AI
AI algorithms thrive on data. Whether it's training data for ML models, vast datasets for deep learning networks, or real-time data for AI-driven applications, the demand for data is insatiable. However, this data deluge presents a challenge: how to efficiently store, access, and process colossal amounts of information in a fraction of the time.
AI Workload Optimization and Processing Power
High-performance and AI workload optimized storage solutions are the bedrock upon which AI computations are built. These systems offer rapid data access and high-speed processing, essential for handling the complex calculations and vast datasets inherent in AI tasks. Whether it's training neural networks, running predictive analytics, or executing real-time AI applications, speed, and data access efficiency is paramount.
Challenges and Innovations
The quest for high-performance storage in the AI domain has challenges. Balancing speed, capacity, cost, and data integrity remains a constant pursuit. However, advancements in solid-state drive (SSD) technologies like NVMe, Zoned Namespaces, and Flexible Data Placement continue to push the boundaries of what's achievable.
Silicon Motion's Leadership in the Storage Industry:
Empowering Tomorrow's Technology Today
Silicon Motion Technology Corporation is a trailblazer in driving technological advancements that shape our digital world. With a rich history spanning over two decades, Silicon Motion has continuously delivered cutting-edge solutions and revolutionized the storage landscape.
Leadership in NAND Flash Controllers
At the heart of Silicon Motion's success lies its expertise in NAND flash controllers. These controllers are the backbone of high-performance, high-capacity solid-state storage solutions. The company's innovative controllers power a myriad of devices, from edge AI devices to enterprise storage systems, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Contact UsInnovation at Its Core
What sets Silicon Motion apart is its unwavering commitment to innovation. The company's relentless pursuit of technological excellence has led to groundbreaking advancements in flash memory management, error correction, and data integrity—paving the way for faster, more efficient storage solutions.
Silicon Motion's Enterprise-grade PCIe Gen5 MonTitan™ SSD Development Platform: Built for Dataceter and Enterprise Applications
Silicon Motion's MonTitan™ is a high-performance, user-programmable PCIe Gen5 development platform targeting the most challenging Datacenter and Enterprise SSD solutions. It is available with the production-ready SM8366 flash controller ASIC, turnkey and layered enterprise firmware, and SSD Reference Design Kits (RDK) to meet compressed time-to-market design schedule, optimizing the total cost of ownership (TCO).
With best-in-class performance, power, and high-capacity support, MonTitan is ideal for today's data center challenges and emerging high-performance computing (HPC), Edge computing, and AI applications.
MonTitan supports the NVM Express 2.0b, and OCP Data Center NVMe SSD 2.0 specifications with firmware optimized for power and performance in standard form factors including E1.S (9.5/15/25 mm), E3.S, and U.2.
Key Differentiation of MonTitan:
Leveraging Silicon Motion's proprietary PerformaShape™ and NANDCommand™ technology, MonTitan delivers superb performance and QoS with industry-leading security.
PerformaShape™
Configured in firmware, PerformaShape™ is a multi-stage shaping algorithm to optimize SSD performance on a per user-defined QoS set bases. Combined with using true hardware isolation technology, the SM8366 ensures maximum bandwidth performance while maximizing user-defined individual performance elements (QoS, Latency, RR/RW, power).
NANDCommand™
The latest PCIe Gen5 x4 NVMe SSD controller maximizes enterprise NAND functionality by utilizing its 5th generation LDPC engine, machine learning, comprehensive real-time media scan, data retention, and endurance extension algorithms. These algorithms are efficiently combined with high-performance soft-decoding, multi-pass and multi-plane handling, smart buffer management, and fine granularity of read/write partitioning for optimized command of next-generation low latency TLC/QLC NAND.
MonTitan also stands out from the crowd by supporting two key enterprise-class features that make it the perfect platform to support the latest QLC NAND:
Zone Namespaces (ZNS)
ZNS, part of the NVMe 2.0 specification, represents a modern approach to storage management that enhances collaboration between the host system and storage devices, enabling improved storage efficiency and capacity. This architecture organizes storage devices, such as SSDs, into zones, allowing for optimized data placement and access. By aligning data writes with the physical characteristics of the storage media, ZNS reduces write amplification and extends the lifespan of the device, making it ideal for applications requiring high performance and reliability.
Here's how Zoned Namespaces work:
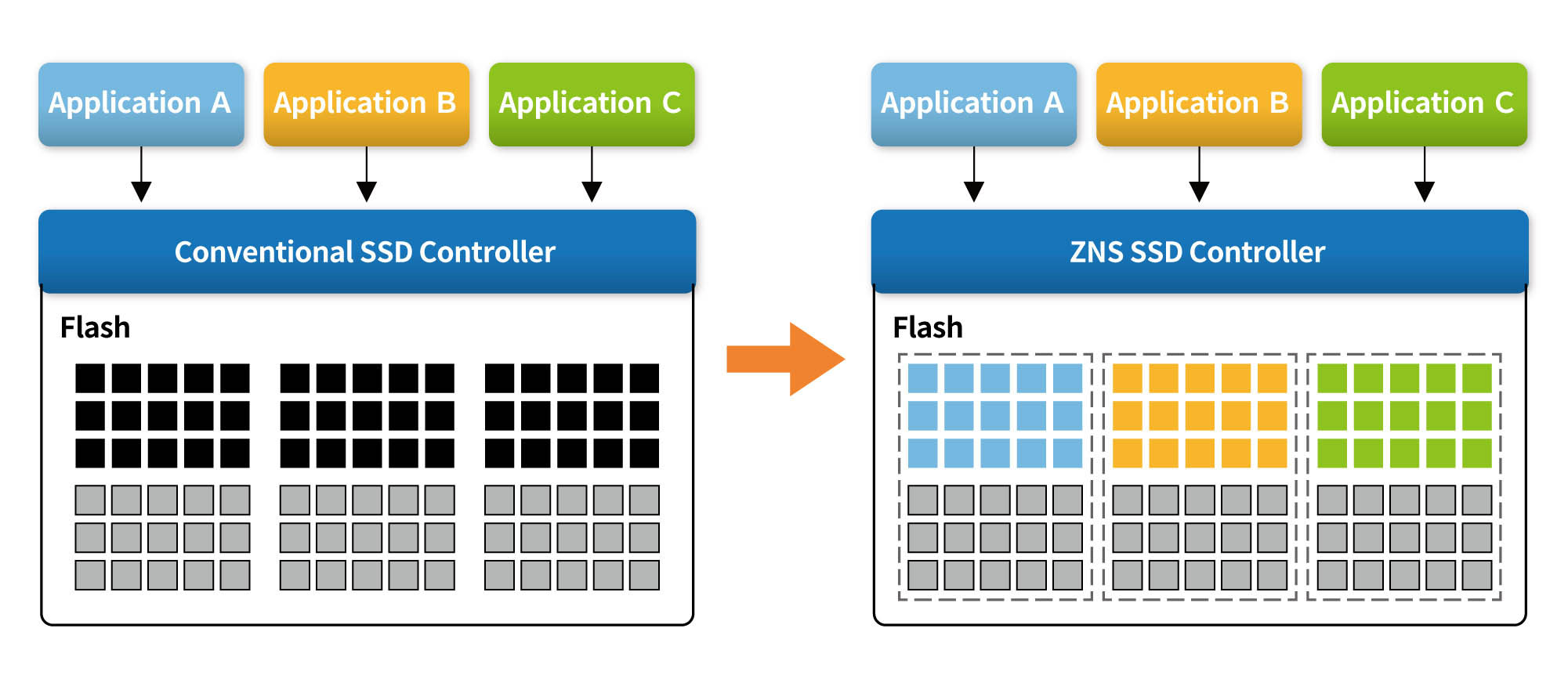
Source: Zoned Storage https://zonedstorage.io/docs/introduction/zns
1. Zoning Storage Devices:
Zone Creation: Storage devices, typically SSDs, are logically divided into zones with varying attributes, such as different performance or capacity characteristics. These zones are managed by the host system or storage controller. Sequential Write-Only Zones: Zoned Namespaces often include zones optimized for sequential write operations. These zones allow for efficient large-block sequential writes, enhancing performance for specific workloads.
2. Logical-to-Physical Mapping:
Mapping Data to Zones: The host system or storage controller maps incoming data to specific zones based on predetermined criteria. This mapping considers factors like data type, access frequency, and performance requirements.
3. Zone Awareness:
Zone-Aware Applications: Applications and file systems are designed to be "zone-aware," meaning they understand the zoned storage architecture. They interact with the storage system, providing directives on data placement aligned with the zoning scheme.
SSDs that support ZNS do not require large quantities of DRAM to implement the Flash Translation Layer (FTL), hence reducing on-board DRAM footprint and cost. The act of implementing Zone Storage on the host allows the system software and hardware to work together more efficiently by eliminating the multiple (duplicated) levels of indirection required for logical to physical mapping between the host and the SSD controller and the file system to the device. ZNS also reduces the need for over-provisioning and removes the issues associated with write amplification and QoS variability.
In short, ZNS addresses the issues of scale, QoS and TCO, which hinder conventional SSDs. The architecture of a ZNS SSD yields the following characteristics:
- Garbage Collection - Minimal required for a ZNS SSD
- Over-provisioning - Virtually none needed
- Write amplification - Because of serial writes, this is 1 or very close to 1
- Small amount of DRAM - Minimal required to manage incoming data caching
Additionally, although TLC and QLC flash technologies offer higher capacities, they cannot sustain the same number of write cycles offered by SLC flash. ZNS opens the door to mixed technology SSDs that comprise both SLC flash (providing high endurance) and TLC/QLC flash (providing high capacity) to be effectively utilized.
Flexible Data Placement (FDP)
Flexible Data Placement (FDP) is an adjacent technology to Zone Namespaces.
FDP is a newly ratified NVMe specification (TP41461) that aims to simplify and reduce modification to host software and driver while achieving similar data placement optimization benefits of ZNS. The new standard was driven by Meta, Google, and Samsung, who aligned efforts to fast-track the FDP specifications.
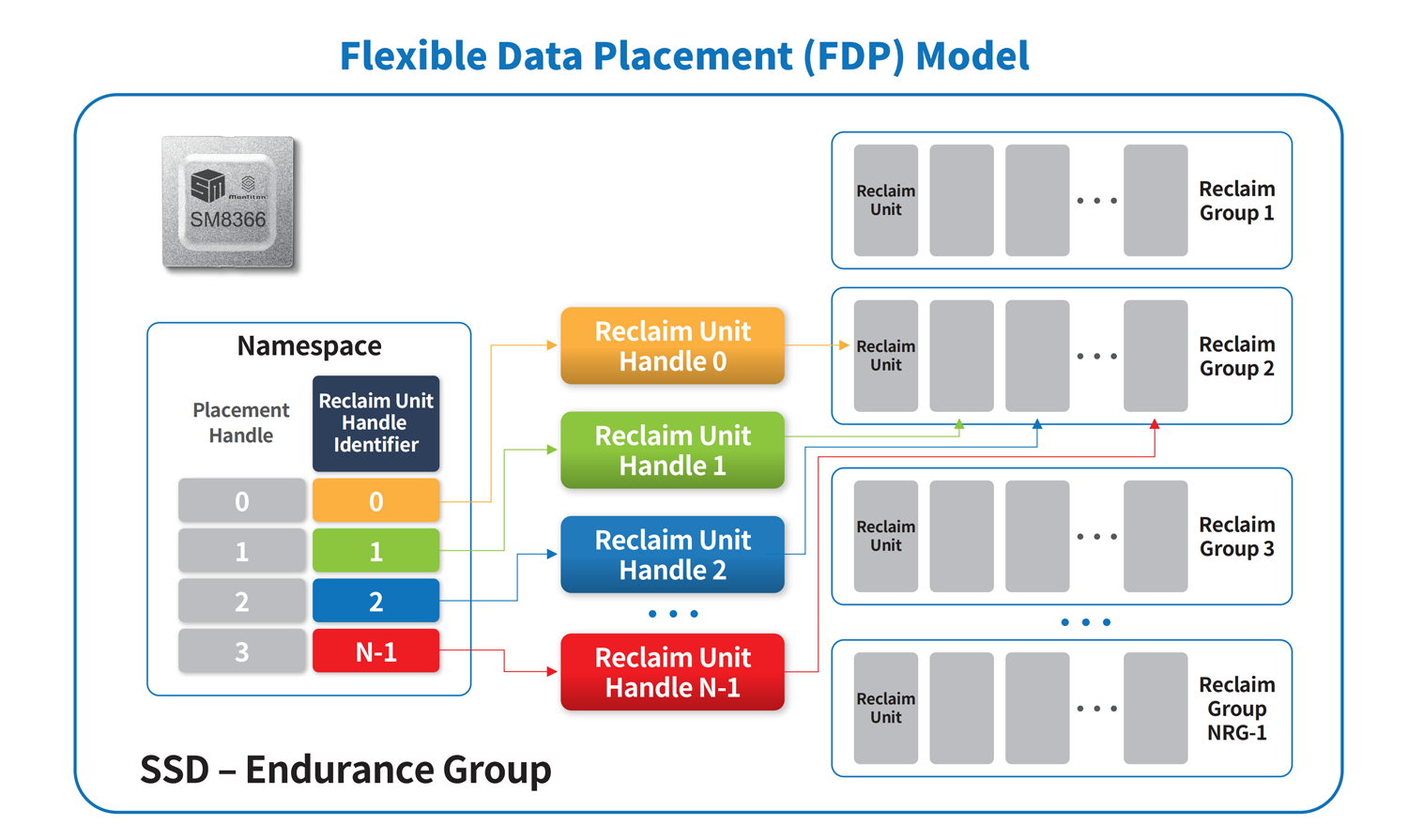
The key advantage of FDP is its backward compatibility with legacy systems and reduction in engineering resources needed to deliver system-level optimizations. FDP accomplishes this by targeting the first 80% of host/device cooperation for better data placement, where any required changes to existing software stacks are not overly intrusive.
Data placement in an FDP-enabled SSD improves upon today's disaggregated storage model by enabling data segregation through 'hint' provided to the host about where to allocate data on the SSD. FDP-enabled SSDs accomplish this by exposing superblock information, which allows the host to tag writes to specific Reclaim Units (RU) so that the device can align data from multiple applications.
This host/device cooperation reduces write amplification (WA), the incidental data that is created when data is written by the host to the media, and provides guarantees for de-allocating RUs which gives the host power to orchestrate garbage collection (GC).
MonTitan, Developed for Tomorrow's AI World, is Sampling Today:
By supporting the above industry-leading enterprise-class SSD features, MonTitan is designed to address tomorrow's AI world storage need and it is available for production today. Both the SM8366 - high-performance PCIe Gen5 x4 NVMe enterprise SSD controller, and its Reference Design Kits (RDKs) are available for customer to order.

The MonTitan Reference Design Kits (RDKs) are available in two different configurations: Conventional NVMe and the market's first QLC-based PCle Gen5 Zoned Namespaces SSDs. Each RDK is purpose-built to support tturnkey firmware that is power and performance-optimized per application with < 25W SSD average power and < 5W Idle SSD power.
With best-in-class performance, power, and high-capacity support, MonTitan is ideal for today's data center challenges and emerging HPC, Edge, and AI applications.
It can be foreseen that in the future, all enterprises will embark on digital transformation projects. As AI/ML applications continue to deepen, the demand for data will inevitably increase. At this juncture, enterprises need to rely on high-quality storage solutions that can perfectly balance performance, capacity, cost, and data integrity. Only then can they provide optimal processing capabilities for various AI workloads.
Learn more about MonTitan: https://www.siliconmotion.com/products/enterprise/detail
Contact Us